Trees in the urban landscape play a significant role in enhancing the well-being of its citizens by offering numerous benefits to communities, wildlife and environment. Green spaces help people re-connect with nature, their neighbours and surroundings.Trees not only add character to the surroundings but perform vital biological functions like photosynthesis and prevents soil erosion by holding and absorbing water during intense rainfall. They also enhance the bio-diversity of the space by hosting a number of bees, butterflies, birds, lizards, bats and other species of wildlife. They improve the air quality by absorbing pollutants and by intercepting harmful particulates that are emitted by vehicles and industries. Effective planning and implementation of efficient policies towards protecting the trees and nurturing the urban eco-systems are of utmost importance to achieve an ecologically sustainable urban growth.
About the book:
The Pollachi Papyrus, in collaboration with Tungsten Creative, brings to you a comprehensive guideline for transplantation of trees in an abstract format aided by photographs, outlining the methods adopted and procedures followed during the transplantation project along the Pollachi – Coimbatore highway.
These ‘Guidelines on Tree Transplanting’ will serve as a general reference, designed and developed with a view to providing systematic steps in assessing the feasibility and suitability of transplanting trees in a urban landscape during development projects. The book will guide you through ascertaining the project feasibility at the planning stage and help identify the major considerations in design, documentation, implementation and post construction stages for proper tree transplanting works and the after-care.
Download the book in pdf here
What is Transplantation?
Transplanting is the term used to describe the digging and replanting of a grown tree from one location (host site) to a new location (receptor site).
A delicate process that involves science & engineering
Due to the wide extent and morphology of tree root system, transplanting of trees usually involves substantial removal of roots in a scientific manner. The whole transplanting process in particular for large trees is an engineering feat and requires substantial involvement of resources and time.
1. Identification of trees
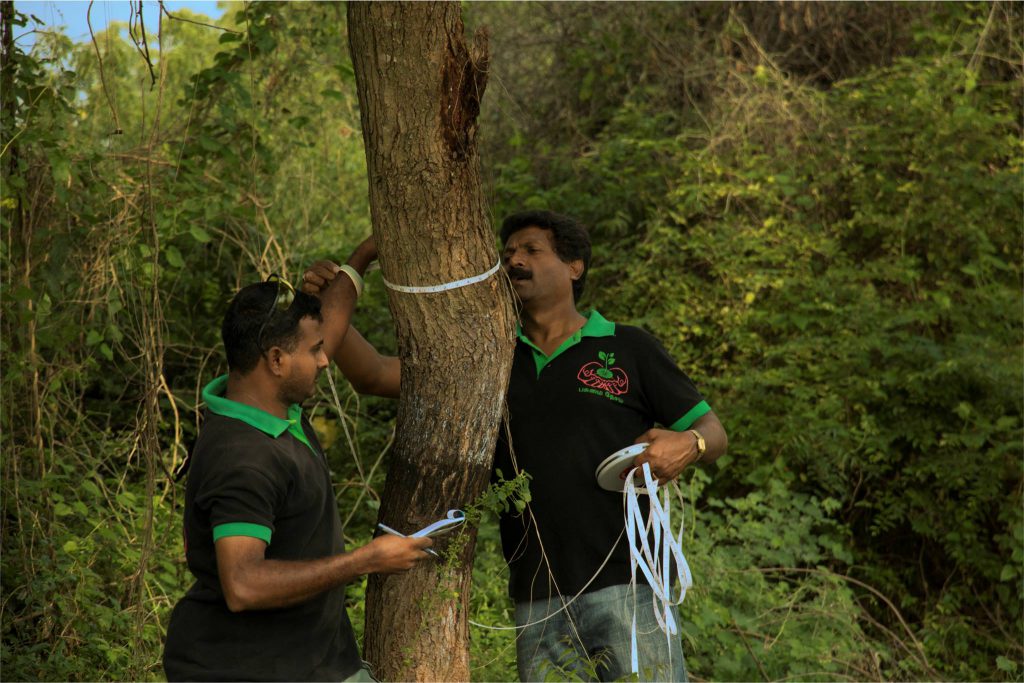

Trees should be properly preserved and no tree should be unnecessarily removed while implementing development projects. Trees that are suitable for and worthy of preservation need to be identified during the planning or feasibility stage.
Health
Trees that are healthy and structurally sound, in particular native species need to be identified for transplanting. Digging a tree for transplanting can remove as much as 90 percent of the absorbing roots which causes a ‘transplant shock’ to the tree. A transplanted tree should be able to re-establish sufficient roots to sustain itself. If the tree has poor health, the rates of survival and recovery will be low.
Size
The size of trees that can be re-located is limited by logistical practicability and resource availability. As a general rule, transplanting a small tree can be more successful than the large ones of the same species. The logistical requirements and the cost of moving also increase substantially with the plant size, especially for off-site transplanting.
Species
Invasive or Exotic species that are not native to the region and species that have proven unsuccessful in the past transplantation efforts can be avoided. Trees having particular significance and high conservation value should be considered for transplanting.
For Example: In the Coimbatore region – Neem, Peepal and Ficus tree species have successfully regenerated after transplantation.
2. Identification of Location:

Once the tree is identified, the location ideal for the transplantation (receptor site) of it has to be fixed. Location of the receptor site should preferably be in proximity to the project site to reduce cost factors. This will also maximise the chances of re-generation as close proximity means similar soil composition and climatic conditions – factors that are essential for a successful re-generation. The soil at the receptor site will have to be a similar type, with similar drainage and sun exposure for the tree to thrive. Measures have to be taken to ensure availability of sufficient space to accommodate the tree and guarantee its future growth.
3. Preparation of Receptor Site:
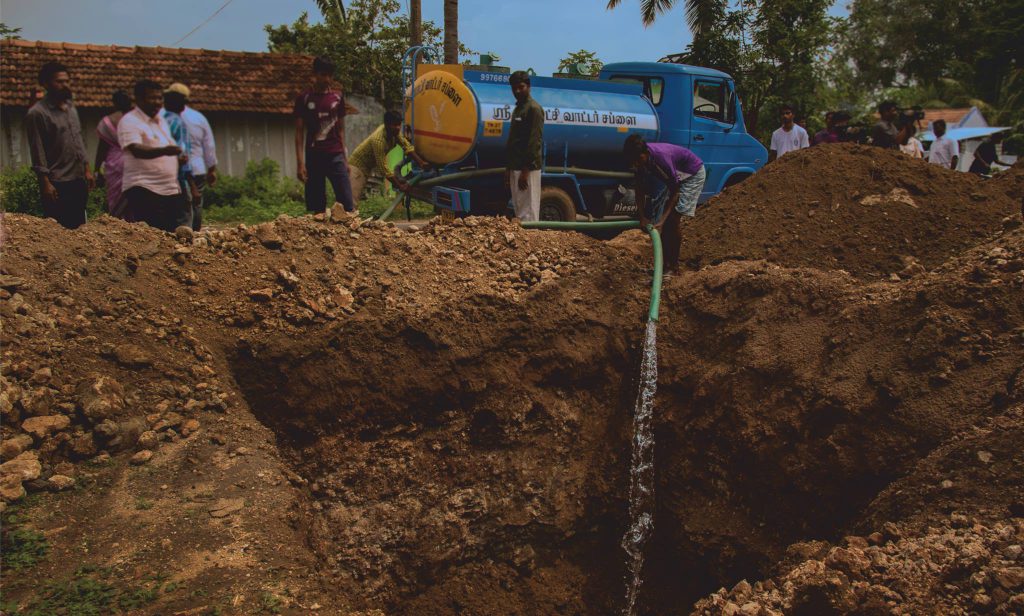

Adequate time has to be allotted to season the receptor site and thereby making it ideal for tree growth. This begins with the pit digging at the receptor site. The depth of the planting pit shall not exceed the depth of the root ball and the width should follow international practice – a minimum of 1.5 times the diameter of the rootball to suit the location. The pit should be dug atleast a day before the identified tree is uprooted. It has to be watered well and let to cool-off for a minimum of eight hours before transplantation. If the soil is extremely hard or compacted, the pit dug should be much larger to loosen the soil around the perimeter and to make it easier for the roots to spread when they begin to grow outward. The existing top soil ploughed from digging should be stripped and put aside for re-use as much as possible.
4. Crown Pruning:
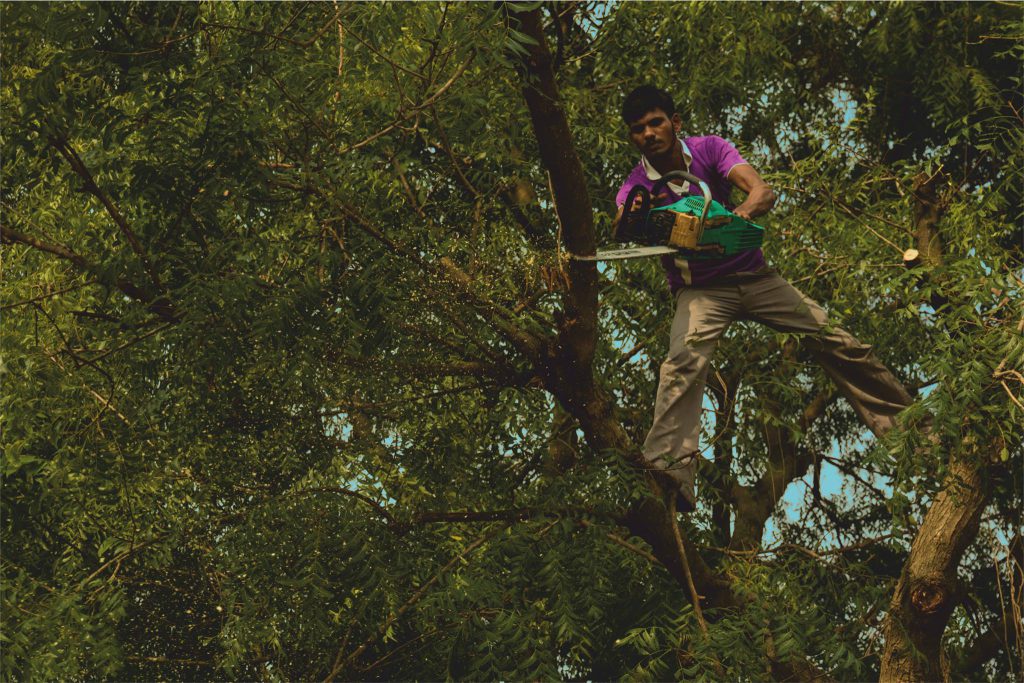

Pruning of tree crown during transplanting may not be necessarily beneficial to the trees as thinning the crown can reduce the tree’s capability in producing food and building up reserves. Excessive pruning can ruin the natural form of a tree and reduce photosynthesis. However, controlled pruning is necessary to reduce risk and inconvenience to public while transporting it from the host site to receptor site. In some cases, pruning may also be done to improve the tree health and structure by removing the pest infested branches or towards the general enhancement of its appearance.
5. Uprooting & transfer:
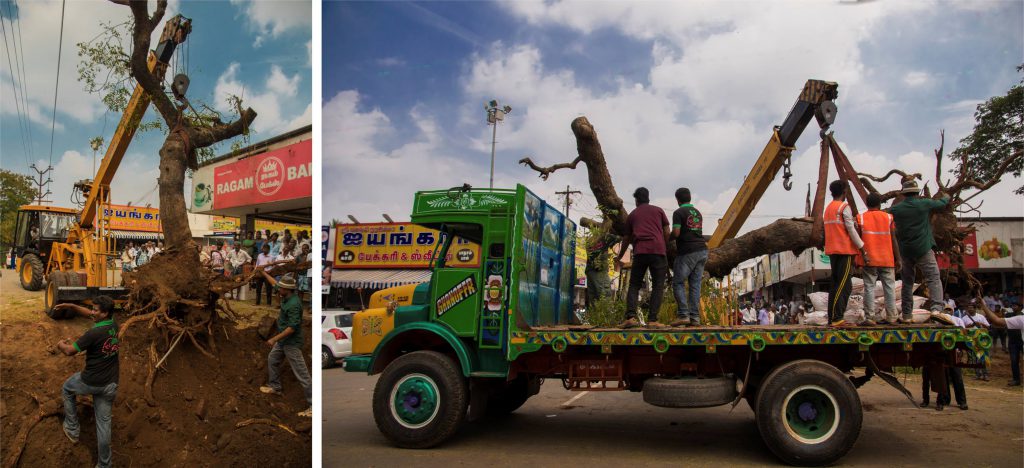

The tree should be pulled up with most of the roots still intact in the soil while the soil around the root ball should not wither off. With the help of sharp ends of the JCB, the root system of the sapling should be dug around. Cuts should be made from the base of the tree, as deep as possible, so that the roots are preserved and intact. Lifting should be done with padded protection for the tree, using a crane connected to the support around the main trunk of the tree. It is essential to make sure that self-tightening slings around the trunk does not bruise or rupture the bark else it could lead to tree death. Once lifted up, the tree should be tipped to a horizontal position on a trailer to be transported to the receptor site.
6. Planting:
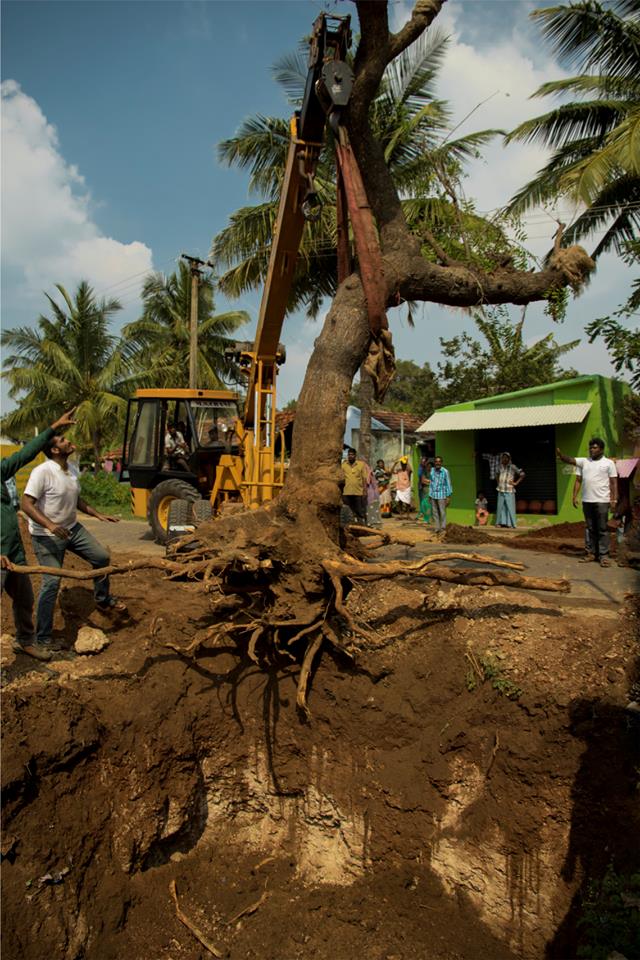

At the receptor site, the previously dug pits should be filled with one unit of native soil from the host site, mixed with coir peat, natural manure and set as layer from the bottom of the pit. This will avoid a distinct interface between the soil at the planting pit and the native soil from the host site. Trees will not tolerate highly compacted soil, which should be broken up, over as large an area of the site as possible. Planting pits should be provided with drainage to allow effective percolation of water.
First Aid:
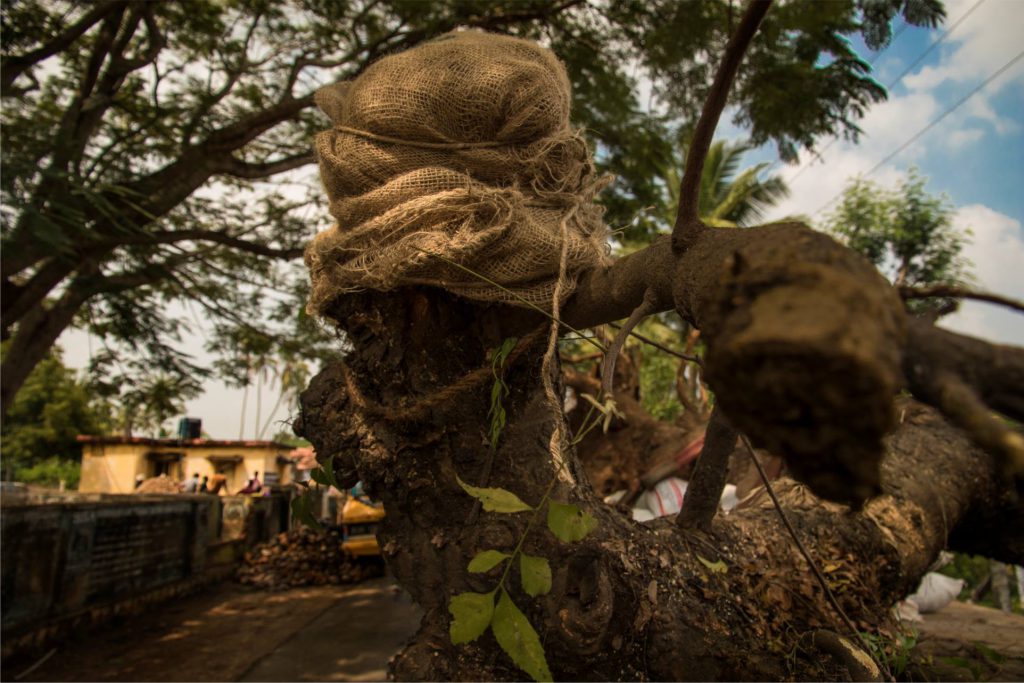

Before the tree is planted, the bruised branches (from crown pruning and transfer) should be smeared and covered with cow dung. After applying the dung, wet hessian sacks should be tied around the cut branches to avoid direct exposure to sunlight. This will prevent damage to vital tissues and encourages and fastens the re-generation of leaves from the cut area.
While planting, the tree should be placed in the same orientation from which they originated. The top surface of the root ball should not be below the surrounding soil. Once the tree is in position, the back-fill soil, that comprises of both native soil from host site and soil dug out from the pit at receptor site shall be reinstated and it shall not be compacted to a density that inhibits root growth. The back-fill soil should be tamped firmly around the base to stabilise the tree, but the rest of the soil should be tamped only lightly, or left to settle on its own. Water should be added to the root ball and the backfill to bring the root ball to field capacity.
7. Post-planting care:
All newly planted trees are subject to stress until a normal spreading root system starts developing. The primary objective of planning site preparation is to provide a quantity of back-fill soil that promotes rapid initial root development and does not restrict root spread beyond the planting hole. It would be necessary to ensure the tree is stable before its root system is fully recovered to give support. Proper care after transplanting will help assure survival and minimise stress and ensure a higher successful rate. Maintenance is a continuation of the transplanting process. Efforts and expenses can be wasted if trees are not given proper care after transplanting.
Hay Wrapping:
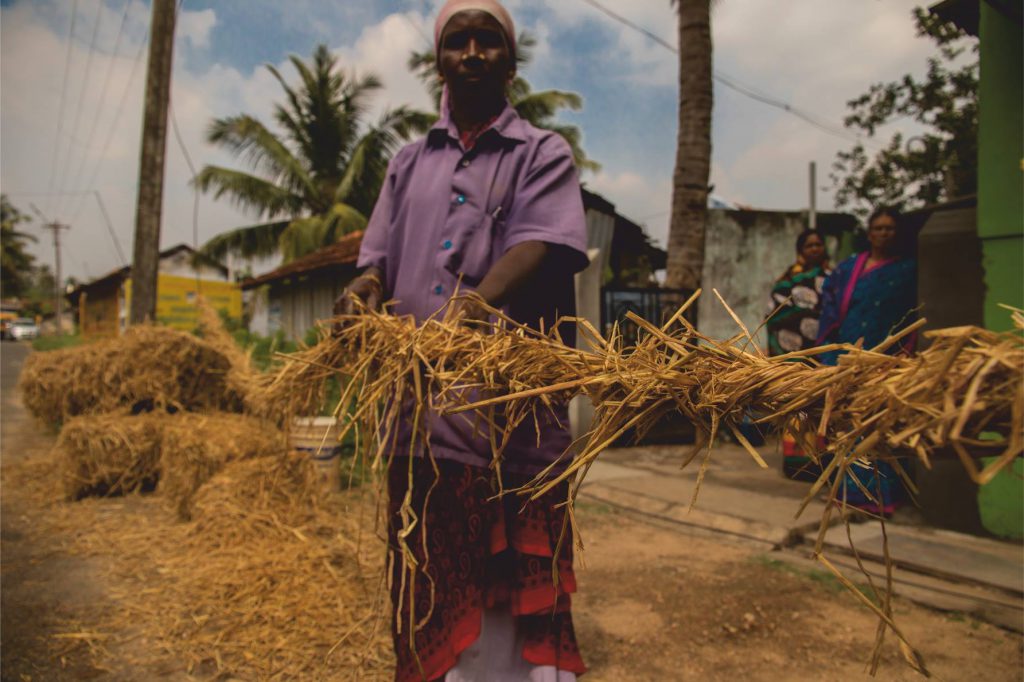

In order to prevent exposure to excessive sunlight and to retain sufficient moisture, the transplanted, stressed tree should be wrapped from the top to the base part that is above the soil with hay bales, that can be procured from market as needed and manually strung into ropes to suit the purpose. Once wrapped, water should be sprayed all over to dampen the hay-covered area.
Mulching:
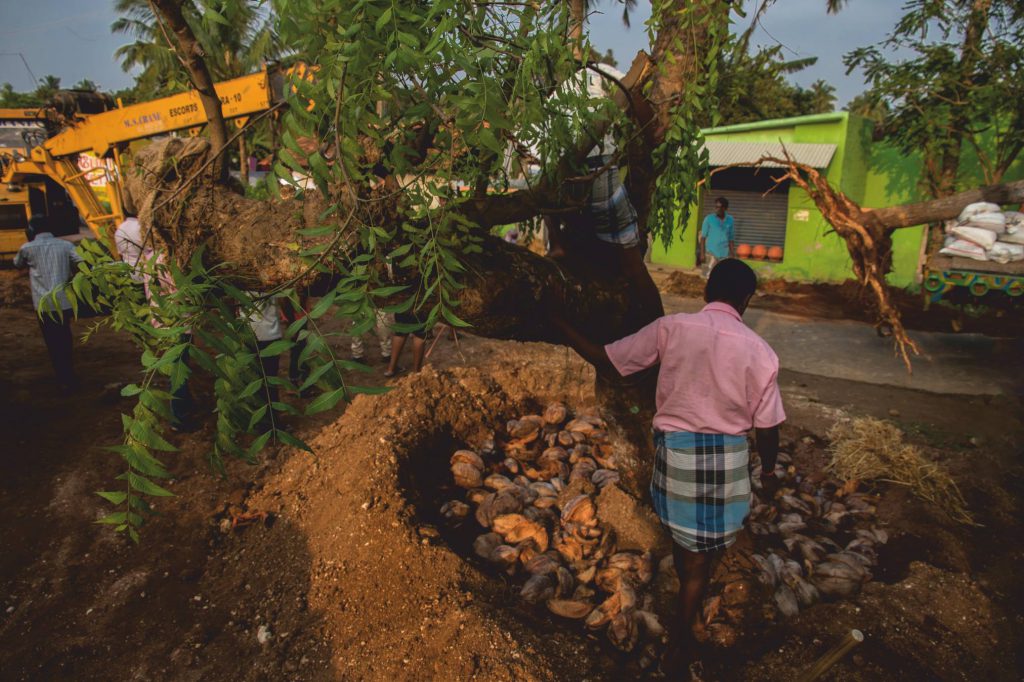

Mulch can be used to conserve soil moisture by buffering soil temperature extremes, to control weed growth and other competing vegetation, and to replenish organic matters and nutrients in the soil. A mix of Coir peat and coconut shells can be used for the purpose. A well-established layer of mulch can hold more water than the soil itself, without decreasing soil aeration. The mulch used should be free from pests and diseases. Moderate release of nutrients by decomposition of both mulch and organic matter added to back-fill soil may be sufficient during the initial period.
Watering:
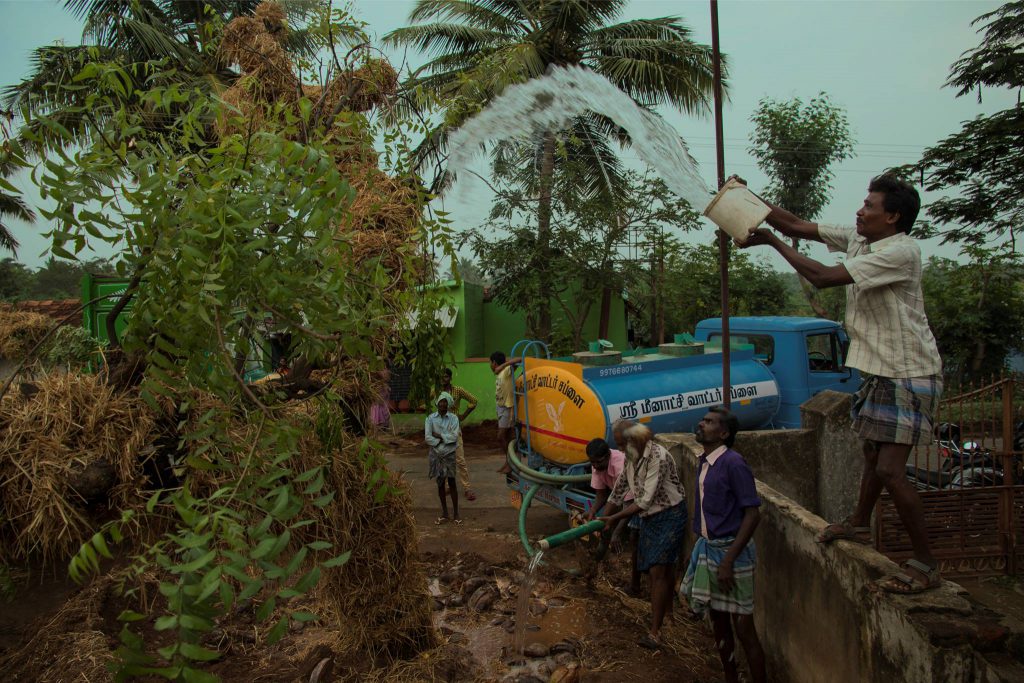

Sufficient and appropriate watering is important for the proper root growth. Provision should be made for watering, allowing for total wetting of the rooting volume to minimise stress and assure survival. Fertilisation may be unnecessary unless nutrient deficiency is confirmed.
Tree transplanting should be conducted in a controlled and safe manner. Workers who are involved in transplanting trees should be given adequate instruction, supervision and safety measures to ensure that tasks are completed in a safe manner. The sites shall be inspected for possible hazards prior to beginning any transplanting procedure. The location of utilities and other obstructions both below and above ground shall be taken into consideration prior to transplanting any tree.
Duties and Responsibilities:
Government Departments of various fields need to be intimated, and they should carry out prior inspection and approve of the activity at the host site as well as receptor site. The process to transplant the trees was overseen by a committee headed by the District Collector and Sub-Collector, who along with various government department and NGOs identified the trees to be re-located and assigned the respective roles and duties to various departments are mentioned in the book.

The Way Forward:
Though Pollachi is considered as a land of natural wealth and prosperity, rapid economic developments are causing damage to its urban environment and ecology. Though transplantation is an encouraging option, steps should be considered to avoid cutting as many trees as possible to save the remaining green cover of Pollachi. Exploring alternative routes, considering better engineering designs and improved public service transportation like railways etc., during road widening projects, will have a beneficial effect on climate, public well-being and economy of the region.
Download the book in pdf here






